Present Continuous Tense
How do we make the Present Continuous Tense?
How do we use the Present Continuous Tense?
We use the present continuous tense to talk about:
action happening now
action in the future
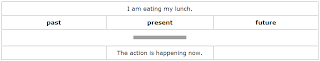
Present continuous tense for action happening now
a) for action happening exactly now
Look at these examples.
Right now you are looking at this screen and at the same time...
...the pages are turning.
...the candle is burning.
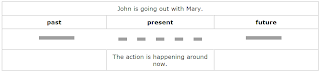
b) for action happening around now
The action may not be happening exactly now, but it is happening just before and just after now, and it is not permanent or habitual.
Look at these examples:
- Muriel is learning to drive.
- I am living with my sister until I find an apartment.
Present continuous tense for the future
We can also use the present continuous tense to talk about the future - if we add a future word!! We must add (or understand from the context) a future word. "Future words" include, for example, tomorrow, next year, in June, at Christmas etc. We only use the present continuous tense to talk about the future when we have planned to do something before we speak. We have already made a decision and a plan before speaking.
Look at these examples:
- We're eating in a restaurant tonight. We've already booked the table..
- They can play tennis with you tomorrow. They're not working.
- When are you starting your new job?
In these examples, we have a firm plan or programme before speaking. The decision and plan were made before speaking.
How do we spell the Present Continuous Tense?
We make the present continuous tense by adding -ing to the base verb. Normally it's simple - we just add -ing. But sometimes we have to change the word a little. Perhaps we double the last letter, or we drop a letter. Here are the rules to help you know how to spell the present continuous tense.
Present Continuous Tense Quiz
Now check your understanding »
===================================
Present Continuous
زمن المضارع المستمر
زمن المضارع المستمر
في البداية ماذا نعني بالزمن المضارع المستمر؟
What do we mean by the term Present Continuous?
لو نلاحظ من الإسم (مستمر ) أي مازال في الإستمرار
بعكس المضارع البسيط فقد ينتهي بعد مدة معينة .
إذا هو الزمن الذي يعود على حدث لفعل معين يحدث الآن في هذا الوقت
إذا هو الزمن الذي يعود على حدث لفعل معين يحدث الآن في هذا الوقت
ومازال الحدث مستمرا وقد يتوقف وقد لايتوقف إذا الحدث مستمر وليس في الماضي أو المستقبل .
* متى نستخدم الفعل المضارع المستمر؟
When do we use the Present Continuous?
إذا في حالات معينة تستخدم المضارع المستمر تعالوا مع بعض نشوف هذه الحالات:
أولا/ في حالة التعبير عن عمل أو حدث أو نشاط معين بأنه مازال مستمرا
* متى نستخدم الفعل المضارع المستمر؟
When do we use the Present Continuous?
إذا في حالات معينة تستخدم المضارع المستمر تعالوا مع بعض نشوف هذه الحالات:
أولا/ في حالة التعبير عن عمل أو حدث أو نشاط معين بأنه مازال مستمرا
في الوقت الذي يتكلم فيه الشخص .وهذا الحدث في زمن المضارع الحالي
.وهذا العمل والحدث من المحتمل أن ينتهي في المستقبل . وغالبا ما تستخدم هنا كلمة
Now
أمثلة / Examples
Naser and Mohammad are playing football now .
ناصر ومحمد يلعبون الآن كرة القدم
إذا لو نلاحظ هنا الحدث هنا هو لعب كرة القدم وهذا الحدث مازال مستمرا الآن
Now
أمثلة / Examples
Naser and Mohammad are playing football now .
ناصر ومحمد يلعبون الآن كرة القدم
إذا لو نلاحظ هنا الحدث هنا هو لعب كرة القدم وهذا الحدث مازال مستمرا الآن
في زمن التكلم وقد ينتهي قريبا في المستقبل القريب أي قد ينتهي ناصر
ومحمد من لعب الكرة بعد ساعة أو ساعتين .
إذا الحدث هنا فيه إستمرارية ((اللعب بالكرة))
لذلك نستخدم المضارع المستمر وليس المضارع البسيط .
ثانيا/ في حالة التعبير عن عمل أو حدث أو نشاط معين حدث في الماضي
لذلك نستخدم المضارع المستمر وليس المضارع البسيط .
ثانيا/ في حالة التعبير عن عمل أو حدث أو نشاط معين حدث في الماضي
ومازال مستمرا في وقت المتكلم ومن المحتمل أن هذا الحدث قد يستمر
في المستقبل لوقت غير محدد والذي قد يكون إما زمن طويل أو قصير .
أمثلة / Examples
Salem is working for an oil company.
يعمل سالم في شركة للبترول.
إذا الحدث هنا وهو ((العمل في الشركة )) بدأ في الماضي وهو مازال
أمثلة / Examples
Salem is working for an oil company.
يعمل سالم في شركة للبترول.
إذا الحدث هنا وهو ((العمل في الشركة )) بدأ في الماضي وهو مازال
مستمرا الآن أي أن سالم مازال يعمل في الشركة وعمل سالم في
الشركة سيتمر في المستقبل إلى أجل غير محدد . إذا الحدث
هنا ((العمل)) يدل على الإستمرارية وعدم الثبات لذلك لا نستخدم المضارع البسيط.
Mary is studying music in New York.
تدرس ماري الموسيقى في نيويورك.
الحدث هنا هو ((دراسة الموسيقى)) بدأ في الماضي وهو مازال مستمرا
Mary is studying music in New York.
تدرس ماري الموسيقى في نيويورك.
الحدث هنا هو ((دراسة الموسيقى)) بدأ في الماضي وهو مازال مستمرا
الآن أي أن ماري مازالت تدرس الموسيقى ودراستها ستستمر في المستقبل
إلى أجل غير محدد . إذا الحدث هنا ((الدراسة )) تدل على الإستمرارية
وعدم الثبات لذلك لانستخدم المضارع البسيط.
ثالثا/ قد نستخدم المضارع المستمر للتحدث عن حدث أو عمل سوف يحدث
ثالثا/ قد نستخدم المضارع المستمر للتحدث عن حدث أو عمل سوف يحدث
في المستقبل .وفي هذه الحالة نستخدم كلمة
أو عبارة أو شبه جملة تدل أن الحدث سيحدث في المستقبل.
أمثلة / Examples
We are buying anew car as soon as the new models come out.
سنشتري سيارة جديدة قريبا في الوقت الذي تظهر فيه الموديلات الجديدة .
إذا الحدث هنا وهو ((شراء السيارة )) هذا الحدث سيحدث قريبا
أمثلة / Examples
We are buying anew car as soon as the new models come out.
سنشتري سيارة جديدة قريبا في الوقت الذي تظهر فيه الموديلات الجديدة .
إذا الحدث هنا وهو ((شراء السيارة )) هذا الحدث سيحدث قريبا
أي في المستقبل القريب وشراء السيارة حدث مستمر يدل على الاستمرارية
ولهذا إستخدمنا المضارع المستمر .وكذلك إستخدمنا كلمات تدل على المستقبل مثل
As soon as
The new student is arriving next week.
الطالبة الجديدة ستصل الأسبوع القادم.
إذا الحدث هنا وهو ((وصول الطالبة الجديدة )) هذا الحدث سيحدث قريبا
As soon as
The new student is arriving next week.
الطالبة الجديدة ستصل الأسبوع القادم.
إذا الحدث هنا وهو ((وصول الطالبة الجديدة )) هذا الحدث سيحدث قريبا
أي في المستقبل القريب ووصول الطالبة حدث مستمر يدل على الاستمرارية
ولهذا استخدمنا المضارع المستمر .وكذلك إستخدمنا كلمات تدل على المستقبل مثل
Next week
رابعا / في حالة التحدث عن حدث غالبا مايحدث
Next week
رابعا / في حالة التحدث عن حدث غالبا مايحدث
ويتكرر .وفي هذه الحالة نستخدم كلمة always
مثال/Example
My young son always is learning new things.
إبني الصغير عادة مايتعلم أشياء جديدة.
وقد يكون التحدث عن شيء يتكرر غالبا قد لايرضي
مثال/Example
My young son always is learning new things.
إبني الصغير عادة مايتعلم أشياء جديدة.
وقد يكون التحدث عن شيء يتكرر غالبا قد لايرضي
المتكلم أي أنه لايكون راضيا عما يحدث
مثال
Wake up ! you are always sleeping.
إستيقظ أنت عادة ماتنام .
إذا المتحدث غير راضي هنا عن المخاطب في عادة النوم الكثير .
خامسا/ في حالة التحدث عن حدث متكرر الحدوث
مثال
Wake up ! you are always sleeping.
إستيقظ أنت عادة ماتنام .
إذا المتحدث غير راضي هنا عن المخاطب في عادة النوم الكثير .
خامسا/ في حالة التحدث عن حدث متكرر الحدوث
سواء هذا الأسبوع أو هذا الشهر أو هذه السنة.
أمثلة / Examples
I am taking five course this semester.
أنا آخذ خمسة كورسات هذا الترم .
إذا الحدث هنا هو دراسة الكورسات التي تتكرر خلال هذا الترم .
She is writing another book this year.
هي تكتب كتابا آخرا هذه السنة .
إذا الحدث المتكرر هذه السنة هو كتابة الكتاب الآخر .
· & كيف نصيغ الفعل المضارع المستمر؟
How to form The present Continuous ?
منعا لتداخل الأمور في بعضها قسمت الصياغة إلى ثلاث أقسام ..
ولكن قبل التطرق إلى هذه الثلاثة أقسام أود أقول أن الشيء الذي يميز
أمثلة / Examples
I am taking five course this semester.
أنا آخذ خمسة كورسات هذا الترم .
إذا الحدث هنا هو دراسة الكورسات التي تتكرر خلال هذا الترم .
She is writing another book this year.
هي تكتب كتابا آخرا هذه السنة .
إذا الحدث المتكرر هذه السنة هو كتابة الكتاب الآخر .
· & كيف نصيغ الفعل المضارع المستمر؟
How to form The present Continuous ?
منعا لتداخل الأمور في بعضها قسمت الصياغة إلى ثلاث أقسام ..
ولكن قبل التطرق إلى هذه الثلاثة أقسام أود أقول أن الشيء الذي يميز
صياغة المضارع المستمر هو إضافة (ing) ملحقة بالفعل ومسبوقة بفعل مساعد
أي (is-am- are)
والآن هيا بنا إلى الثلاثة أقسام :
أولا/
I + am + V -ing
إذا حرف I ثم الفعل المساعد am (لأنه حرف ال I ماياخذ إلا الفعل المساعد am)
أي (is-am- are)
والآن هيا بنا إلى الثلاثة أقسام :
أولا/
I + am + V -ing
إذا حرف I ثم الفعل المساعد am (لأنه حرف ال I ماياخذ إلا الفعل المساعد am)
ثم الفعل الأساسي ملحق به ال (ing)
مثال
I am reading a nice story now.
أنا أقرأ قصة جميلة الآن.
ثانيا/
( she-he-it) + is + V (ing)
إذا أولا إما إحدى الضمائر المفردة التالية She-he -it
مثال
I am reading a nice story now.
أنا أقرأ قصة جميلة الآن.
ثانيا/
( she-he-it) + is + V (ing)
إذا أولا إما إحدى الضمائر المفردة التالية She-he -it
ثم الفعل المساعد is ثم الفعل ملحقا ب (ing)
أمثلة ..
She is trying to improve his work .
هي تحاول أن تحسن من عملها .
It is raining.
إنها تمطر .
ثالثا/
(we-you-they)+ are+ V (ing)
إذا أولا إما إحدى الضمائر الجمع التالية we-you-they
أمثلة ..
She is trying to improve his work .
هي تحاول أن تحسن من عملها .
It is raining.
إنها تمطر .
ثالثا/
(we-you-they)+ are+ V (ing)
إذا أولا إما إحدى الضمائر الجمع التالية we-you-they
ثم الفعل المساعد are ثم الفعل ملحقا به ال (ing)
أمثلة:
They are sleeping now.
هم نائمون الآن.
You are singing beautifully.
أنت تغني بعذوبة .
ملاحظة / لابد من فهم القاعدة جيدا ثم حفظها منعا ((لللخبطة))!!!
· هناك أفعال لايمكن صياغتها على هيئة المضارع المستمر
أمثلة:
They are sleeping now.
هم نائمون الآن.
You are singing beautifully.
أنت تغني بعذوبة .
ملاحظة / لابد من فهم القاعدة جيدا ثم حفظها منعا ((لللخبطة))!!!
· هناك أفعال لايمكن صياغتها على هيئة المضارع المستمر
لأنها في الواقع لاتدل على الإستمراية وإنما تدل على حالة معينة ووضع معين
وعدم الإستمرارية لذلك من سابع المستحيلات صياغتها في شكل المضارع المستمر
ولكن في هيئة المضارع البسيط وهي :
أولا / الأفعال التي تعود إلى وظائف العقل
Mental state
أولا / الأفعال التي تعود إلى وظائف العقل
Mental state
(know-realize-understand-recognize-
believe-feel-suppose-think-imagine-
doubt-remember-forget-want-need-prefer-mean)
مثال
من الخطأ أن نقول
مثال
من الخطأ أن نقول
He is knowing.
والصحيح هو
He knows
ثانيا/ الأفعال التي توضح إنفعالات معينة
Emotinal state
(love-like-appreciate-hate-dislike-fear-envy-mind -care)
ثالثا/ أفعال تدل على الملكية
Possesion (posses-have-own-belong)
رابعا/ أفعال الحواس الخمس
Sense perception
(taste-smell-hear-feel-see)
خامسا/ أفعال أخرى تدل على حال معين وعدم الإستمرارية
(seem-look-appear-cost-owe-weigh-be-exist-consist of- contain-include)
* كيف نصيغ النفي في الجملة المثبتة:
How to form the negative?
كما هو معروف حينما نريد صياغة أي نفي في اللغة الإنجليزية نقوم فقط بوضع كلمة not للنفي
مثال
They are sleeping now.
هم نائمون الآن .
هذه الجملة مثبتة وحينما نريد نفيها نضيف فقط not بعد الفعل المساعد سواء كان
Is-am-are
فتصبح الجملة :
They are not sleeping now.
هم غير نائمون الآن.
* كيف نصيغ الأسئلة في المضارع المستمر؟
How to form Questions in Present Continous
نضع الفعل المساعد في البداية ثم الفاعل سواء أكان